Home / Blog / Technology / What are the main international standards for low-voltage electrical equipment?
What are the main international standards for low-voltage electrical equipment?
By:QUISURE Updated:August 25,2024 14:07PM
1. What are the main international standards for low-voltage electrical equipment? What do the abbreviations and names represent?
| IEC | Standards of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) |
| CE | European Standards (EN) |
| UL | Underwriters Laboratories Standards (UL) |
| NEMA | National Electrical Manufacturers Association Standards (NEMA) |
| ANSI | American National Standards (ANSI) |
| VDE | Association for Electrical, Electronic & Information Technologies Standards (VDE) |
| DIN | German Industrial Standards (DIN) |
| NF | French Standards (NF) |
| JIS | Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) |
| BS | British Standards (BS) |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing and Materials Standards (ASTM) |
| AFNOR | French Standardization Association Standards (AFNOR) |
2. 3C Certification

2.1. Introduction to 3C Certification
3C is the abbreviation for the certification mark "CCC," which stands for "China Compulsory Certification." The 3C certification, or China Compulsory Certification, is a mandatory certification system established by the Chinese government to ensure consumer safety, national security, and strengthen product quality management. It was introduced by the Chinese government in 2001 and officially implemented in 2002. The 3C certification is the most fundamental safety certification standard within China. Any product that falls within the mandatory certification catalog and is sold, imported, or manufactured in the Chinese market must obtain 3C certification.
2.2. Industry Scope of Certification
The 3C certification applies to a wide range of products, covering, but not limited to, the following categories:
• Electric wires and cables: Such as power cables, communication cables, optical cables, etc.
• Electrical devices for switching, protection, or connection: Such as circuit breakers, power strips, switches, electrical outlets, etc.
• Household appliances: Such as refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, electric fans, rice cookers, water heaters, etc.
• Lighting equipment: Such as fluorescent lamps, LED lighting fixtures, desk lamps, etc.
• Motor vehicles: Such as passenger cars, trucks, motorcycles, and their components.
• Information technology equipment: Such as computers, printers, monitors, etc.
• Audio and video equipment: Such as televisions, sound systems, DVD players, etc.
• Low-voltage electrical equipment: Such as low-voltage circuit switches, control devices, cable assemblies, etc.
• Toys: Children's toys, educational toys, etc.
2.3. Geographic Scope of Certification
The 3C certification primarily applies to products that are sold, imported, or manufactured within China. Whether these products are produced domestically in China or imported, they must comply with the 3C certification requirements. This means that any relevant products entering the Chinese market, regardless of their country of origin, must pass 3C certification to be sold in China.
3.TüV Certification

3.1. Introduction to TüV Certification
TüV (Technischer Überwachungs-Verein) means Technical Inspection Association in English. TüV testing is similar to China's Technical Quality Supervision Bureau. Initially, each state in Germany had its own independent TüV organization, but unlike state agencies, these TüV organizations were independent third-party entities rather than government bodies, although they undertook many state-authorized tasks. Over time, through mergers and acquisitions, the largest TüV organizations in Germany are now TüV SÜD (previously known as TüV PS in China) and TüV Rheinland. The main areas of TüV's business include product certification, system certification, inspection, and industrial services, such as product safety certification (GS) - voluntary certification, quality system certification, and ROHS testing, among others.3.2. Industry Scope of TüV Certification
TÜV certification applies to a wide range of industries and sectors, including but not limited to the following categories:- Machinery and equipment manufacturing: Including industrial machinery, construction machinery, elevators, lifting equipment, etc.
- Automotive industry: Testing and certification of vehicles and components, such as headlights, braking systems, emission testing, etc.
- Electronics and electrical products: Such as household appliances, information technology equipment, power tools, lighting products, etc.
- Medical devices: Safety certification and testing for various medical instruments and equipment.
- Construction and infrastructure: Certification related to building materials, structural safety, energy systems, etc.
- Energy and environment: Certification of renewable energy equipment such as solar photovoltaic systems, wind power equipment, and environmental technologies.
- Food and beverages: Food safety management system certification, safety testing of packaging materials, etc.
- Aerospace and railways: Safety and quality certification for systems and equipment related to aerospace and railway transportation.
- Chemical products: Testing for the safety and environmental compliance of chemicals.
3.3.Geographic Scope of TüV Certification
The TüV mark is a safety certification mark specifically designed by German TüV for component products, and it is widely accepted in Germany and Europe. Companies can also apply for a CB certificate in conjunction with the TüV mark application, which allows them to obtain certifications from other countries through conversion. Additionally, once a product has passed TüV certification, TüV Rheinland will recommend these products to manufacturers who are searching for certified component suppliers, and during the process of certifying the final product, components that have obtained the TüV mark may be exempted from further inspection.4.CE Certification

4.1. Overview of CE Certification
The CE mark is a mandatory marking that indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). CE stands for "Conformité Européenne," meaning "European Conformity." By obtaining CE certification and affixing the CE mark, a product is declared to meet the essential requirements of the relevant European directives. This certification allows the product to be legally sold in the European Community market. Products that fall under the scope of these directives must have the CE mark to be sold; otherwise, they cannot be marketed. If a product already bearing the CE mark is found not to meet safety requirements, it must be withdrawn from the market. Continuous non-compliance with the CE marking regulations may result in restrictions, prohibition from entering the EU market, or forced withdrawal from the market.4.2. Industry Scope of CE Certification
CE certification applies to a wide range of product categories across various industries and sectors. The main applicable industries include, but are not limited to, the following:- Electrical equipment: Such as household appliances, power tools, lighting equipment, information technology equipment, etc.
- Machinery: Including industrial machinery, agricultural machinery, construction machinery, etc.
- Personal protective equipment: Such as safety helmets, protective gloves, safety shoes, protective eyewear, etc.
- Medical devices: Ranging from simple bandages to complex medical equipment, including in vitro diagnostic medical devices.
- Construction products: Such as building materials, windows, doors, insulation materials, etc.
- Toys: Including children's toys, educational toys, electronic toys, etc.
- Pressure equipment: Such as boilers, pressure vessels, pipelines, valves, etc.
- Equipment for explosive atmospheres: Such as explosion-proof electrical equipment, control devices, sensors, etc.
- Radio and telecommunications terminal equipment: Including mobile phones, radio transmission equipment, network communication devices, etc.
- Measuring instruments: Such as scales, metering pumps, thermometers, etc.
- Chemicals: Chemical substances and preparations must comply with REACH and CLP regulations.
4.3. Geographic Scope of CE Certification
CE certification mainly applies to EU member states and countries within the European Economic Area (EEA). However, due to its global recognition, many other countries and markets also acknowledge or accept the CE mark. The specific regions where CE certification applies include:- EU member states: The CE mark is mandatory in all EU member states, and any products entering these markets must meet CE certification requirements.
- European Economic Area (EEA): Includes EU member states as well as Iceland, Norway, and Liechtenstein. CE certification is also applicable in these countries.
- Switzerland and Turkey: Although not EU member states, Switzerland and Turkey also require the CE mark for many products.
- Other global markets: While CE certification is primarily aimed at the European market, it is widely recognized in other regions (e.g., the Middle East, Africa, Asia), particularly in markets heavily influenced by EU standards.
5.CB Certification

5.1. Overview of CB Certification
The CB scheme (IEC System for Conformity Testing and Certification of Electrotechnical Equipment and Components) is an international system operated by the IECEE. Under this system, the certification bodies of IECEE member countries test the safety performance of electrotechnical products based on IEC standards. The test results, namely the CB Test Report and CB Test Certificate, are mutually recognized among the IECEE member countries. IECEE is the abbreviation for the International Electrotechnical Commission’s System for Conformity Testing and Certification of Electrotechnical Equipment and Components.5.2. Industry Scope of CB Certification
CB certification mainly applies to electrical and electronic products. The applicable industry scope includes, but is not limited to, the following categories:- Household appliances: Such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, rice cookers, microwaves, water heaters, etc.
- Information technology equipment: Such as computers and peripherals, servers, printers, routers, etc.
- Audio and video equipment: Such as televisions, audio equipment, DVD players, camcorders, etc.
- Lighting equipment: Including various types of lamps, such as fluorescent lamps, LED lights, chandeliers, etc.
- Power tools: Such as electric drills, electric saws, electric hammers, electric screwdrivers, etc.
- Office equipment: Such as copiers, fax machines, telephones, scanners, etc.
- Telecommunication terminal equipment: Including landline phones, mobile communication devices, etc.
- Electrical accessories: Such as switches, sockets, circuit breakers, wires, cables, etc.
- Measuring instruments: Such as ammeters, voltmeters, power meters, etc.
5.3. Geographic Scope of CB Certification
The geographic scope of CB certification covers the IECEE member countries, which are spread across the globe. The main regions include:- IECEE Member Countries: Currently, IECEE has over 50 member countries, including most European countries, the United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Australia, China, India, Russia, Brazil, South Africa, etc. Manufacturers can use CB certification to export products to these countries and apply for local certification marks.
- Global Scope: Although CB certification is mainly aimed at IECEE member countries, due to its international nature and the uniformity of standards, many non-member countries also recognize CB test reports and certificates as the basis or reference for entering their markets. Manufacturers can greatly simplify the process of global market access for their products through the CB system.
6.UL Certification

6.1. Introduction to UL Certification
UL is the abbreviation for Underwriters Laboratories Inc. UL is the most authoritative safety testing organization in the United States and one of the largest non-governmental institutions globally engaged in safety testing and certification. It is an independent, non-profit organization dedicated to testing for public safety.- UL1077 Certification: This certification is mainly for products used as components, which will be applied to complete end products or systems listed by UL and will not be used independently. Instead, they are used as components in equipment that UL tests.
- UL489A Certification: This indicates that the circuit breaker can be considered a complete product that has been tested by UL and meets the safety standards recognized in the United States. It effectively protects against measurable risks such as fire, electric shock, and other related damages. The product is produced under UL’s follow-up service plan. The certification is based on the UL489A standard—Circuit Breakers for Communications Equipment.
6.2. Industry Scope of UL Certification
UL certification applies to a wide range of industries and product categories, primarily including the following fields:- Electrical and electronic products: Such as household appliances, information technology equipment, audio and video equipment, lighting equipment, etc.
- Industrial equipment: Including industrial control equipment, factory automation equipment, power tools, etc.
- Building materials and systems: Such as wires and cables, piping systems, fire alarm systems, fire-resistant materials, etc.
- Consumer products: Including household kitchen equipment, personal care devices, portable electronic devices, etc.
- Medical devices: Such as diagnostic equipment, therapeutic devices, monitoring devices, etc.
- Automotive industry: Including automotive parts, in-vehicle electronic devices, electric vehicle charging systems, etc.
- Fire safety products: Including fire extinguishers, smoke detectors, fire alarms, etc.
- Chemicals and materials: Including plastics, rubber, coatings, adhesives, etc., used to test their flammability, toxicity, and other characteristics.
- New energy products: Such as solar photovoltaic modules, wind energy equipment, energy storage systems, etc.
6.3.Geographic Scope of UL Certification
Products entering the U.S. market must obtain UL certification. The UL mark is a recognized safety certification mark in the U.S. and North America.- Listing: The UL listing mark on a product indicates that a sample of the manufacturer’s complete product has been tested by UL and meets the applicable UL requirements.
- CLASSIFIED: Products with this mark have been evaluated for a limited range of hazards or specific applications.
- Component Recognition: To speed up the evaluation of products or systems and save costs, components that are incomplete or have limited performance can undergo component recognition for use in future products or systems listed or classified by UL. Using UL-certified components in any final product does not imply that the product itself is UL-listed.
- United States: UL certification is crucial for safety in the U.S., and many state and local regulations require products sold in the market to be UL certified.
- Canada: Although Canada has its certification bodies (such as CSA), UL certification is also widely accepted in Canada, especially for products sold across borders.
- Global Scope: Although UL certification is primarily for the North American market, it is widely recognized globally due to its rigorous testing standards and high credibility. Many other countries and regions view UL certification as an important proof of product safety when importing products.
- International Market: For manufacturers looking to export products to the U.S., Canada, and other markets with high safety requirements, UL certification is a key gateway to these markets.
7.CSA Certification

7.1. Introduction to CSA Certification
CSA stands for the Canadian Standards Association, which was established in 1919 as Canada's first non-profit organization dedicated to developing industrial standards. Products such as electronics and electrical appliances sold in the North American market require safety certification. Currently, CSA is the largest safety certification organization in Canada and one of the most renowned safety certification bodies in the world. It provides safety certification for all types of products in areas such as machinery, building materials, electrical appliances, computer equipment, office equipment, environmental protection, medical fire safety, sports, and recreation.7.2. Industry Scope of CSA Certification
CSA certification covers a wide range of industries and product categories, primarily including the following fields:- Electrical and electronic products: Such as household appliances, information technology equipment, industrial electronic devices, etc.
- Industrial equipment and control systems: Including industrial control equipment, power tools, factory automation equipment, etc.
- Building and construction products: Such as wires and cables, piping systems, HVAC equipment, fire and alarm systems, etc.
- Consumer products: Including household kitchen equipment, lighting equipment, personal care devices, etc.
- Medical devices: Such as diagnostic equipment, monitoring devices, medical electrical equipment, etc.
- Gas equipment: Including gas furnaces, water heaters, stoves, heating systems, etc.
- Energy and renewable energy equipment: Such as solar photovoltaic modules, wind power equipment, electric vehicle charging stations, etc.
- Safety and protective products: Including personal protective equipment, safety helmets, protective eyewear, etc.
- Chemicals and materials: Such as plastics, rubber, coatings, building materials, etc., used for testing properties such as flammability and chemical stability.
7.3. Geographic Scope of CSA Certification
CSA certification primarily applies to the following regions:- Canada: CSA certification is one of the most important safety certification marks in Canada. Many Canadian regulations and standards require electrical products sold in the market to be CSA certified, especially in the fields of construction, industry, and consumer goods.
- United States: Although the U.S. has UL certification, CSA certification is also widely accepted in the U.S. market, particularly for products sold across the North American market. There is a certain level of mutual recognition between CSA and UL, allowing many CSA-certified products to be directly sold in the U.S. market.
- Global Scope: Due to the stringent standards and international recognition of CSA certification, it is also widely recognized globally. Especially in the North American market, CSA certification is seen as an important guarantee of product quality and safety.
- Multinational Companies: For multinational companies looking to export products to the Canadian or North American market, CSA certification is a critical threshold and a competitive advantage for entering these markets.
8.VDE Certification
8.1. Introduction to VDE Certification
VDE is a renowned German testing institution that directly participates in the development of national standards in Germany. Similar to UL, the VDE mark can only be authorized by VDE. In addition to traditional certification for electrical components, wires, cables, and plugs, VDE also issues EMC marks and VDE-GS marks. VDE stands for Prufstelle Testing and Certification Institute, which means the Association for Electrical, Electronic & Information Technologies in Germany. Founded in 1920, it is one of the most experienced testing and certification institutions in Europe. VDE is an EU-authorized CE notified body and a member of the international CB scheme. It is recognized in Europe and internationally by certification systems such as CENELEC for electrical products, CECC for the quality assessment of electronic components, and the IEC for electrical products and electronic components.An overview on VDE certification marks
 |
VDE Mark Electro-technical products including products according to the Product Safety Act (ProdSG) and medical products according to the Medical Product Act (MPG) according to VDE/EN/IEC standards, other technical specifications as well as possible provisions of law with respect to safety and health requirements |
 |
VDE GS Mark Technical working equipment and commodities ready for use, in the sense of ProdSG (optional for such products instead of VDE Mark) according to VDE/EN/IEC standards, other technical specifications as well as possible provisions of law with respect to safety and health requirements |
 |
VDE Cable Mark Cables and insulated cords as well as conduits and ducts according to VDE/EN/HD/IEC standards, other technical specifications as well as possible provisions of law with respect to safety and health requirements |
 |
Cables and insulated cords according to VDE/EN/HD/IEC standards, other technical specifications as well as possible provisions of law with respect to safety and health requirements |
 |
VDE HARmonization Marking Cables and insulated cords according to the HAR certification procedure on the basis of EN/HD standards and specifications of the HAR procedure For more information please visit www.har-cert.com |
 |
VDE EMC Mark Electro-technical products complying with the standards for electromagnetic compatibility on the basis of VDE/EN/IEC/CISPR standards and other technical specifications |
 |
VDE Registration Mark Certificate of Conformity in conjunction with factory surveillance for electro-technical products according to VDE/EN/IEC standards, other technical specifications as well as possible provisions of law with respect to safety and health requirements Quality evaluation of electronic components on basis of VDE/EN/IEC standards and other technical regulations |
 |
ENEC Mark Products according to the ENEC certification procedure on the basis of EN standards and specifications of the ENEC procedure For more information please visit www.enec.com |
 |
ENEC PLUS Mark The ENEC PLUS Mark represents the performance characteristics of productsaccording to the ENEC PLUS certification procedure based on EN standards and specifications. For more information please visit www.enecplus.com |
 |
IECQ CECC Mark Electronic components according to the IECQ procedure on the basis of IEC standards, IECQ/CECC specifications |
 |
KEYMARK The KEYMARK represents performance characteristics of Heat Pumps based on EN standards and specification. |
 |
Special Certificates Proof of special product attributes on basis of relevant EU Directives, laws, standards and special specifications |
 |
System Certificate The System Certificate represents certification of systems and processes based on relevant standards, laws and special specifications. |
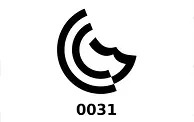 |
G Mark Type Examination for Low Voltage Electrical Products and Appliances in the Middle East. (based onGSO or IEC standards and specification of the GSO procedure) For more information please visit www.gso.org.sa |
8.2. Industry Scope of VDE Certification
VDE certification primarily applies to the following industries and product categories:- Electrical equipment and components: Such as cables, wires, switches, sockets, power connectors, fuses, etc.
- Household appliances: Including refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves, water heaters, ovens, vacuum cleaners, etc.
- Lighting equipment: Such as LED fixtures, fluorescent lamps, desk lamps, chandeliers, and other lighting products.
- Industrial electronics and control equipment: Including inverters, power tools, industrial automation equipment, control panels, etc.
- Information technology equipment: Such as computers and peripherals, network equipment, servers, etc.
- Audio and video equipment: Including televisions, audio systems, DVD players, camcorders, etc.
- Medical equipment: Medical electronic devices, diagnostic instruments, monitoring equipment, etc.
- Electric vehicles: Such as electric bicycles, electric scooters, electric vehicle charging equipment, etc.
- Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) equipment: Filters, inductors, shielding materials used for EMC testing, etc.
- New energy products: Including solar photovoltaic modules, wind power equipment, energy storage systems, etc.
8.3. Geographic Scope of VDE Certification
The geographic scope of VDE certification includes:- Germany: VDE certification is highly recognized in Germany and serves as a crucial safety mark for electrical and electronic products entering the German market. Many products must obtain VDE certification to be sold in Germany.
- Europe: VDE certification is not only widely recognized in Germany but also holds high credibility across Europe. Products with VDE certification typically meet the relevant EU safety standards, such as the CE mark, allowing them to circulate freely within the European Economic Area (EEA).
- Global Scope: Although VDE certification is primarily aimed at the European market, it is widely recognized globally due to its stringent testing standards and high credibility. In markets with high safety requirements, such as Japan, the United States, and Canada, VDE certification can provide a strong competitive advantage for product entry.
- Multinational Companies: For companies looking to sell electrical and electronic products globally, VDE certification is an important guarantee of quality and safety. Particularly when exporting to Germany and the European market, VDE certification can significantly enhance the market acceptance of products.
9.CCS Certification

9.1. Introduction to CCS Certification
China Classification Society (CCS) primarily undertakes the classification services, verification inspection, certification inspection, and statutory services authorized by the Chinese government and foreign (regional) government authorities for domestic and foreign ships, offshore installations, containers, and related industrial products. CCS also performs other approved tasks, such as certification and inspection services for materials used in road transportation, pipeline transportation, and bridges, as well as wind power generation and related specialized equipment.9.2. Industry Scope of CCS Certification
CCS certification primarily applies to the following industries and fields:- Shipbuilding and Repair: Including the design, construction, and repair of various types of commercial vessels, oil tankers, liquefied gas carriers, container ships, bulk carriers, passenger ships, fishing vessels, etc.
- Offshore Facilities and Platforms: Such as offshore oil drilling platforms, Floating Production Storage and Offloading units (FPSO), Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) units, offshore wind power platforms, etc.
- Marine Equipment and Materials: Including the design, production, and testing of marine engines, boilers, pumps, valves, anchor chains, electrical equipment, navigation equipment, etc.
- Marine Engineering: Covering port facilities, submarine pipelines, marine environmental monitoring equipment, etc.
- Crew Training and Certification: Providing training and certification for crew members to ensure they meet international and national standards.
- Watercraft: Including the design and construction of yachts, speedboats, workboats, tugboats, etc.
- Environmental Protection Equipment: Such as ship wastewater treatment systems, exhaust emission control devices, marine environmental protection equipment, etc.
- Shipping and Related Services: Including the evaluation and certification of ship leasing, shipping finance, ship management, and other related services.
9.3. Geographic Scope of CCS Certification
The geographic scope of CCS certification primarily includes the following regions:- China: As the only classification society in China, CCS certification is mandatory in the construction, operation, and repair of ships and marine facilities within China, making it the core certification body in the Chinese market.
- Global Scope: CCS is a full member of the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS), and ships and marine facilities certified by CCS are widely recognized globally, especially in countries and regions with close maritime trade relations with China.
- International Maritime Organization (IMO): CCS plays a significant role in the IMO, and its certification standards typically meet or exceed IMO requirements, giving CCS certification substantial influence in the global shipping market.
- Other Major Maritime Countries: Many countries recognize and accept CCS certification, especially in cases where ships are built in cooperation with China or in marine engineering projects. CCS certification helps ships and marine facilities enter these markets and ensures they meet international standards.
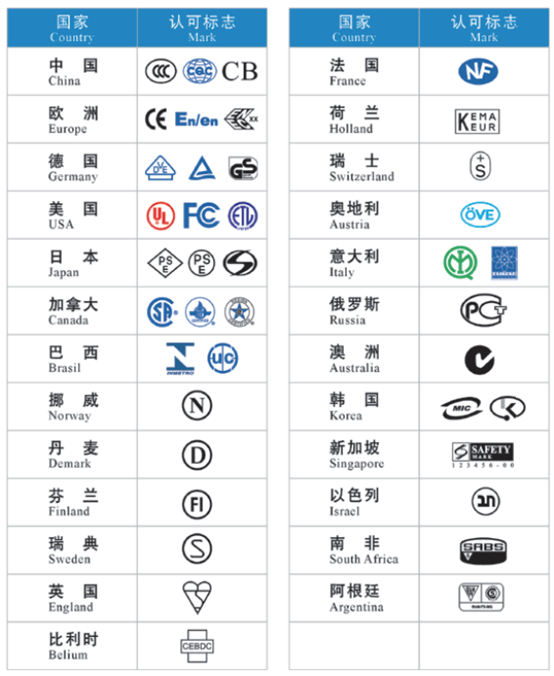
10.Product Certification Marks of Selected Countries